From 2020 to 2021, Dark Web Onion Domains Tor’s anonymity experienced a major change. The Tor software team has rolled out the latest version of its software. It updates the .onion domain look and work. Particularly, the Tor Project has left behind the old 16-character-long .onion domains. It is also known as v2 addresses and replaced them with 56-character-long domains, known as v3. This article about upgraded Tor V3 onion services lets you know only a Third of Dark Web Onion Domains Switched to V3 Deep Web Sites.
The initiative was taken by considering the need to network’s privacy, security, and resilience to deanonymization attacks. And the entire procedure took more than a year to complete.
- Sep 2020 – The Tor Project releases v0.4.4 of the Tor anonymity software. Also, warn server operators that the v2 domain will no longer be produced.
- Jul 2020 – The Tor developers unleash Tor v0.4.6, which blocks server owners from v2 onion domain registration.
- Oct 2021 – The stable versions are released for all Tor categories that remove support for previous v2 domains.
- Nov 2021 – The Tor Project releases Tor Browser 11, which eliminates support for v2 domains.
Adoption of V3 Onion Domains on the Dark Web
You might be aware of Onion sites which are relatively part of the Tor network. It is an anonymous network that offers users to access the internet anonymously. Onion sites contain URLs that end with the “.onion” TLD, such as “example.onion.”
The traffic over Tor Network runs through multiple channels. It encrypts and re-encrypts it at every step, which makes it challenging to trace the origin of the traffic. Anyone interested in Onion sites can access them using the Tor browser to protect user privacy and anonymity.
However, adopting V3 Onion Domains on the Dark Web has introduced more advanced network privacy, security, and resilience to deanonymization attacks.
What are V3 Onion Services?
V3 Onion Services, also known as Tor V3 onion services or Tor hidden services V3. It is an upgraded version of the Tor network’s anonymous and decentralized service architecture.
These services provide enhanced security, improved privacy, and stronger cryptographic protocols than earlier versions of Onion services (V2 and prior).
Bear one thing in mind that transitioning from V2 to V3 onion services is still in process. Conversely, the dark web Tor network supports V2 and V3 onion services.
The coordinated effort pushes dark web users to adopt V3 for its improved security and privacy features. Consequently, some onion services may still use V2, while the recommendations emphasize migrating V2 to V3 for the best security and anonymity.
Major Cause for V3 Transition Dark Web Onion Domains
The major cause of this change is to stay connected with all components of all Onion services.
It aims to provide the relevant information to connect with a specified onion address (just like the DNS system for regular domain names).
Moreover, the hidden service directory is a distributed hash table formed by all Tor relays with the HSDir flag. It protects the privacy of Onion service users.
For V2 onion services, the data published in the hidden service directory is uploaded in plain text form. That means the Tor relays with the HSDir flag can learn a great amount of information about a small fraction of running V2 onion services.
You should not collect or inquire about v2 onion addresses via HSDir relays as Tor Bad relays teams consider its malicious behavior and sanctioned.
The latest version V3 uses encryption and key derivation to address this problem since the V3 address is a public key. All the data with the key is incorporated in the .onion address.
However, clients still require queries from the directory for information about a particular onion address.
With the help of V3 onion services, this is restricted by using key derivation to derive a daily-rotated identifier (“blinded public key”).
So rather than asking the hidden service directory for facebookwkhpilnemxj7asaniu7vnjjbiltxjqhye3mhbshg7kx5tfyd.onion, the Tor client automatically calculates the current identifier from the onion address and the current date (e.g., 2021-08-19), and asks for that blinded public key (here: ek4gJEtlHmwwadLvMNG7tYx/lJuJN1zQl6pMVkGmAcM).
Key Features & Improvements in V3 Dark Web Onion Services

The key features and improvements of V3 onion services include:
Improved Security: V3 onion services use stronger cryptographic algorithms, including the Ed25519 elliptic curve for key generation and the SHA3-256 hash function. These improvements enhance the security of the hidden service and safeguard against potential attacks.
Longer Onion Addresses: V3 services have longer and more complex addresses than V2. Instead of the 16-character base 32-encoded addresses, V3 addresses are 56 characters long. It contains a base32 representation of a 56-byte public key. The longer addresses increase the cryptographic strength and reduce the likelihood of address collapsing.
Enhanced Anonymity: V3 onion services improve resistance against certain attacks, such as guard discovery and correlation attacks. They also provide better resistance to enumeration attacks, making it more difficult for adversaries to identify and track hidden services.
Offline Keys: V3 onion services develop offline keys, allowing operators to generate the keys for their hidden services offline and upload the public key to the Tor network. This separation between the online and offline keys improves security by decreasing the risk of key exposure.
Client Authorization: V3 Onion services offer more flexibility in client authorization. Hidden service operators can create client-specific authorization keys, granting access only to authorized clients. This feature enables better control over access to the service.
Exploring the Status Quo: The State of V3 Deep Web Sites
Despite much effort, the Tor team announced the V3 rollout in advance. The dark web monitoring company compiled and released new numbers. The experts of DarkOwl show that the Tor network is still creating in a larger part of servers operating older v2 domains.
According to the DarkOwl’s Vision platform, an average of 104,095 active .onion services across both addresses sources: 62% are v2 addresses, and 38% are v3 addresses,” the company stated.
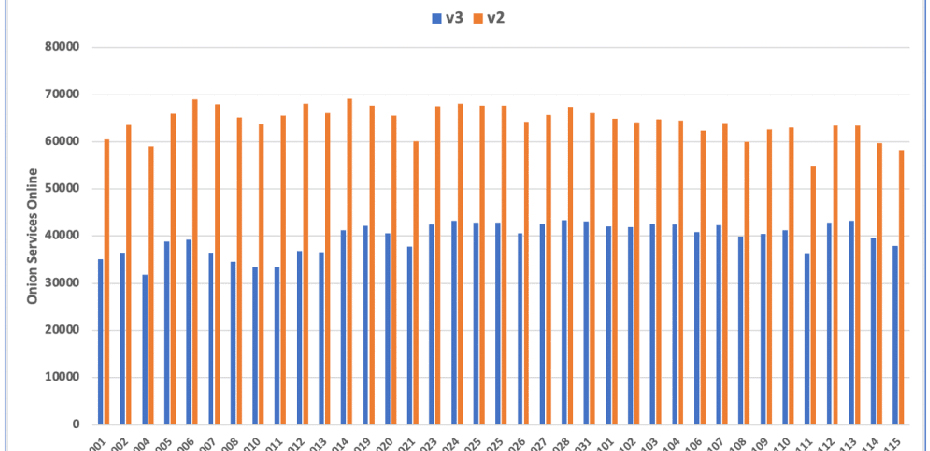
The creation of V3 domains on the dark web gets high in July 2021, coinciding with a Tor project warning that began to appear before v2 domains were approached. That resulted in more than 22,900 v3 domains being registered only in the last weeks of July.
The growth continuously increases as new v2 domains are obsolete, but users can still access existing sites using the older browser versions.
The experts expect v2 sites to disappear next year finally since most Tor host operators will upgrade their servers to versions that no longer support v2 domains.
So there will be no Tor repeaters capable of driving traffic to older generation domains.
Why Have Only a Third of Dark Web Onion Domains Switched to V3?
Indeed, adopting V3 onion services on the dark web has undergone a few challenges, resulting in a relatively slow transition. While the actual reasons for the low adoption rate are multifaceted, several factors contribute to this phenomenon:
Technical challenges: Transitioning from V2 to V3 onion services needs effort and technical command. The changes introduced in V3 were significant, including using new cryptographic algorithms and a revised addressing system. The migration process can be confusing and time-consuming, particularly for operators with limited technical knowledge or resources.
Compatibility issues: V3 onion services are not backward compatible with V2, which means V3 onion domains cannot contact directly with V2 domains. This incompatibility poses a challenge as it requires both the operators of the V3 domains and their users to make the switch simultaneously.
If a significant portion of the dark web still uses V2 services, there may be a reluctance to switch to V3 due to the potential loss of connectivity and users.
Lack of Perks: Some operators may hesitate to adopt V3 onion services because they do not see compelling perks to switch. The V2 services are still functional, and as long as there is no significant disadvantage or pressure to transition, operators may choose to maintain the status quo.
User Resistance: Users of dark web services may also contribute to the slow adoption rate. If the websites they frequently visit or rely on have not transitioned to V3, users may be less motivated to switch browsing habits or install the necessary software updates.
This creates a chicken-and-egg situation, where the lack of user demand hampers the transition, further discouraging operators from adopting V3.
Security Perception: V3 onion services offer enhanced security features compared to V2. There may be a lack of awareness or misconceptions about the benefits.
Some operators might not fully understand the advantages of V3 or believe that their V2 services provide sufficient security for their needs.
It is undeniable that fact obtaining accurate statistics on the adoption rate of V3 onion services can be challenging due to the secretive nature of the dark web. Meanwhile, only a third of onion domains have switched to V3, the actual figures may vary, and the transition rate might have changed.
Benefits of Transitioning to V3 Dark Web Onion Domains

As far as its benefits are concerned in terms of security and privacy, you won’t feel regret transitioning to Version 3 (V3). At the same time, you must note that the deep web is also known as the dark web. The complex place and diverse that hosts legal and illegal activities. The potential advantages of V3 deep websites, assuming they are used for legitimate and lawful purposes.
Enhanced Anonymity: V3 deep websites operate on the Tor network, providing more anonymity than traditional web browsing. Tor routes internet traffic through a series of encrypted relays, making it difficult for anyone to track users’ online activities. This increased anonymity can protect users’ privacy and prevent surveillance.
Protection against Monitoring: By utilizing V3 deep websites, users can mitigate the risk of being monitored by government agencies or malicious actors. This is particularly valuable for individuals in countries with strict internet censorship or surveillance practices. It might be helpful for journalists working on sensitive topics or whistleblowers who wish to remain anonymous.
Resistance to Tracking: V3 deep websites use onion routing, where data packets are encrypted multiple times and routed through various nodes. This method makes it extremely difficult for third parties to trace the origin or destination of the data, thus enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of tracking.
Encryption and Confidentiality: V3 deep websites typically utilize end-to-end encryption, ensuring the content exchanged between users and the site remains confidential. This is especially crucial for communication platforms, file-sharing services, or websites that handle sensitive information.
Access to Restricted Content: Some V3 deep websites host content that may be inaccessible or censored on the surface web due to political, cultural, or legal reasons. This can enable individuals to access information, resources, or unavailable services that are banned or restricted in your region.
Despite these potential benefits, practicing some important precautions when accessing V3 deep websites is important. For the sake of protection from illegal activities and malicious actors also exist within this space. You could face serious legal consequences if you engage in illegal activities on the deep web.
As you know, the deep web is known to host illicit marketplaces, hacking forums, and other nefarious activities. The Deep Web url Includes highly sensitive and guarded information such as Medical records, Government Reports, Financial Records, Email Accounts, Private Messages, Confidential Corporate Web Pages, and Banking Portals.
So users should be mindful of the potential risks and exercise due diligence. Check them out below.
Key Factors to Consider When Visiting Deep Web
We have listed a few prerequisites you must take care of before attempting to access the deep web, whether V2 onion services or V3 onion services. The safest way to visit the dark web is through the Tor Network. For additional safety, you must find out the best VPN services to install and connect and then use Tor in a practice known as Tor-over-VPN.
Many internet service providers (ISPs) and governments may suspect you for the Tor use. Therefore a VPN will do its best to keep your internet activities hidden and prevent anyone from knowing that you’re using Tor.
Get a Reliable & Safe VPN Extension
First, you must hide your IP address and encrypt your internet connection with a trustworthy VPN like AVAST Secure Line VPN. Though they both provide encryption, a VPN and Tor are different.
The installed VPN will block your ISP and any third party from knowing that you’re downloading and using Tor Browser.
Download & Install Tor Browser
The Tor Browser is a free browser that drives traffic through the encrypted Tor network. You can visit the official Tor Project Website to Download Tor Browser because unlicensed third-party downloads may come bunched with malware.
Browse the Dark Web with Tor Browser
With the help of Tor Browser, you can access the .onion domains of the dark web. The dark web is unregulated on a large scale, so avoid visiting dark websites without confirming their authenticity.
Protect Your Identity
The dark website isn’t always scary. However, many scams exist within the space. Try to use encrypted and anonymous email addresses when communicating or taking services from the dark web. You should also pay product costs with an anonymous cryptocurrency wallet.
Eventually, you must install strong security software to protect your device before accessing the dark web.
Gathered Information about V3 onion service
Due to these improvements, V3 onion services leak a small amount of sensitive information. However, these changes do not fully prevent the hidden service directory from revealing interesting metadata.
One can make it possible by estimating the number of running onion services. You may come to know how many numbers of blinded public keys are uploaded because every onion address translates to exactly one blinded public key per day.
This defines it as possible to count onion addresses by counting blinded public keys, which is already used by the Tor Project to gather statistical information about the number of V3 onion services since Tor version 0.4.6.1-alpha.
Hopefully, it will increase earlier as a sufficient number of Tor relays start to report data allowing for reliable V3 statistics. Also, make sure to keep your Tor relays up-to-date.
In addition to more statistical metrics about V3 onion services and their usage, HSDir relays can monitor them by collecting detailed logs of uploads and downloads of blinded public keys.
Let’s assume one could track how many uploaded blinded public keys are never requested or how many client requests for blinded public keys could not be responded to.
How to Encourage the Migration to V3 Onion Domains on the Dark Web?
Following are some of the ways that Tor Network may use in promoting the Migration to V3 Onion Domains on the Dark Web
Awareness: Providing clear and accessible information about the benefits of V3 onion services is crucial. The operators can achieve this through targeted campaigns, tutorials, and documentation explaining the technical advantages, improved security features, and potential long-term benefits of V3.
Collaboration and support: Tor Network team collaborations with developers, operators, and users of dark web services can facilitate the transition.
Through creating forums, online communities, or dedicated channels, individuals can exchange knowledge, seek assistance, and share experiences related to migrating to V3.
Even if Tor the Network team offers technical support and guidance during the transition process, it may explicitly alleviate concerns and barriers.
Incentives and rewards: Incentivizing operators to switch to V3 can help drive adoption. This could involve highlighting the advantages of V3 for their users, such as improved privacy, security, or faster load times.
Additionally, providing rewards or recognition to early adopters or operators who successfully migrate to V3 could encourage others to follow suit.
Continuous research and development: Investing in ongoing research and development of V3 onion services can further enhance their functionality, security, and usability. Addressing existing limitations and actively seeking feedback from the dark web community can help foster confidence and drive adoption.
Conclusion
Wrapping up the entire guide by collecting data and information from different Tor relays depicts only a Third of Dark Web Onion Domains Switched to V3 Deep Web Sites. These experiments and suggestions conclude collecting data from 50 Tor relays which is responsible for only about 1% of the hidden service directory.
Hence, the results provide a good estimation of the total number of V3 onion services. But they are surely not as trustworthy as you would expect for statistics at Tor metrics. Likewise, migration from V2 to V3 onion services has greatly increased throughout 2021.
So if you still use only a V2 onion service, try upgrading V3 onion services into popular dark web browsers, such as Tor. Ultimately, Adopting the V3 transition allows you to receive improved security and anonymity features.
